Understanding HAIs: Ally proteins in the fight against cancer 2022
The key to cure cancer may depend on the understanding of the interplay between the epithelial-derived cancer inducing enzyme matriptase and it´s regulators HAI-1 and HAI-2 may.
Vogel Group has introduced this new terminology ¨Ally protein¨ in order ease the communication of this new and not yet fully understood function of the matriptase inhibitors, in the litteratur.
The previous understanding was that HAIs along with inhibition holds a ¨chaperone-like function¨ although evidence against this is provided by e.g. Yamashita et. al.
Further research of the inhibitory and the ally function of HAIs is necessary to elucidate matriptase associated cancer which might hold the key to cure epithelial-derived cancer.
Published by Vogel Group, February 2022,
first author Annika W. Nonboe

Insights into the regulation of the matriptase-prostasin proteolytic system
2020
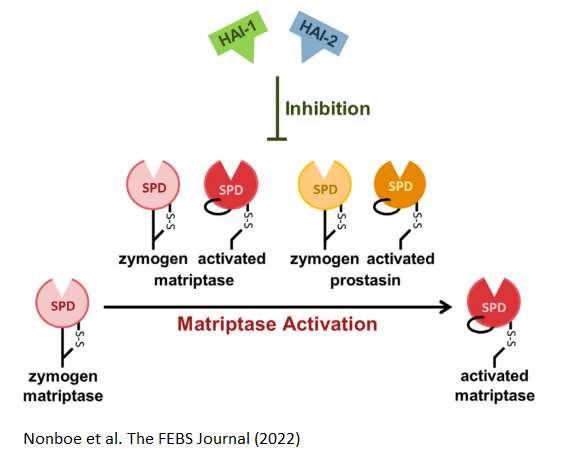
The membrane-associated serine proteases Matriptase and prostasin belong to the S1A subfamily, and are critical for epithelial development and homeostasis.
These two S1A are involved in the activation of each other. The inhibition of matriptase are shown to be facilitated by HAIs, and studies show that matriptase is synthesized in a somewhat active zymogen form.
Previous studies suggest that the zymogen form of
matriptase performs the normal and necessary proteolytic functions of matriptase, whereas excess
matriptase activation likely causes carcinogenesis.
In this paper, we provide strong evidence for an activity of the zymogen form of prostasin, along with an inhibition of this activity, carried out by HAI-1 and HAI-2. Furthermore, we report that zymogen prostasin activates zymogen matriptase but not its own zymogen form.
We propose the existance of an enzyme–enzyme relationship consisting of proteolytically active zymogen forms of both matriptase and prostasin, under control of HAI-1 and HAI-2, located at the pinnacle of an important proteolytic pathway in epithelia.
We propose, that perturbed balance in this proteolytic system, result in rapid and efficient activation of matriptase by the dual action of zymogen matriptase and zymogen prostasin.
Taking together, HAI-1 and HAI-2 is important for
the prevention of matriptase activation whether catalysed by zymogen/activated prostasin
(this study) or zymogen/activated matriptase (previous studies).
Published by Vogel Group, August 2020,
first author Lasse Holt-Danborg.

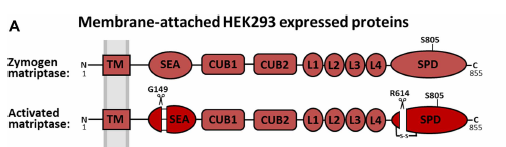
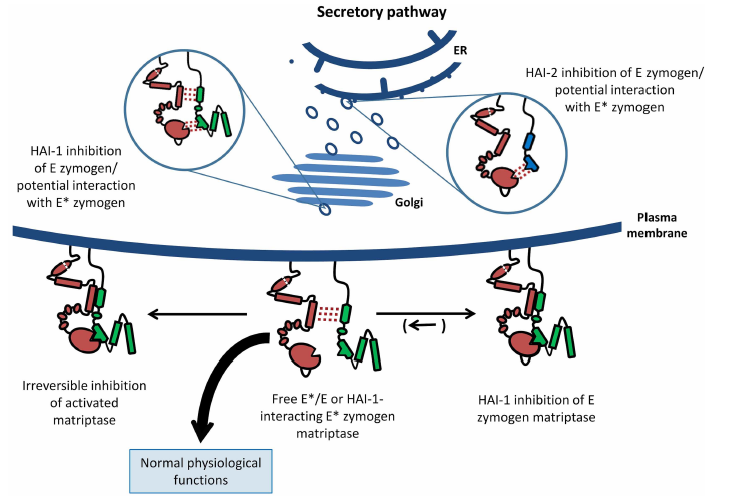
Inhibition of an active zymogen protease the zymogen form of matriptase is regulated
2020
Published by Vogel Group, May 2020.
First author Signe Skovbjerg.

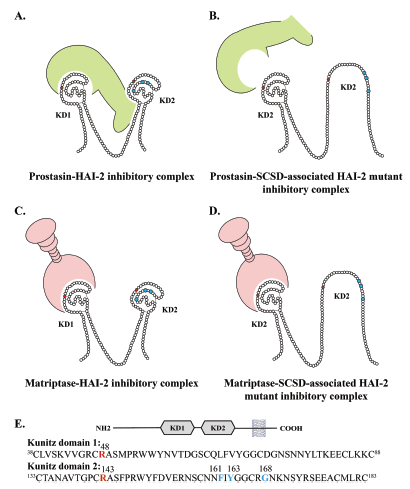
SPINT2 (HAI-2) missense variants identified in congenital sodium diarrhea/tufting enteropathy affect the ability of HAI-2 to inhibit prostasin but not matriptase
2018
In conclusion our data suggests that SCSD is caused by lack of inhibition of prostasin or a similar protease in the secretory pathway or on the
plasma membrane.
The HAI-2 variants
p.Phe161Val, p.Tyr163Cys and p.Gly168Ser
all display decreased ability to inhibit prostasin-catalyzed cleavage.
However, the SCSD-associated HAI-2 variants inhibited matriptase as efficiently as the
wild-type HAI-2.
Homology modeling indicated limited solvent exposure of the mutated amino acids, suggesting that they
induce misfolding of KD2.
This suggests that prostasin needs to engage with an exosite motif located on KD2 in addition to the binding loop (Cys47/Arg48) located on the first Kunitz domain in order to inhibit prostasin.
Published by Vogel Group, November 2018.
First author Lasse Holt-Danborg.

